티스토리 뷰
[CSS Flexbox]
display: flex;위아래 폭은 부모 크기만큼 자동적으로 확장된다. (따로 높이 주지 않아도 된다.)
수평(row) 방향으로 인라인-블록 요소들이 들어간다. (인라인-블록)
[3가지 기억하기]
※ flex-direction : 디폴트는 row 방향 (수직방향, 수평방향)
※ justify-content : 좌우, 중앙 배치 설정
※ align-items : 수직 정렬 (탑, 미들, 바텀)
[flex-grow]
: 비중, 상대크기
<div class="flex-container">
<div style="flex-grow: 1">1</div>
<div style="flex-grow: 1">2</div>
<div style="flex-grow: 8">3</div>
</div>1/10 , 1/10, 8/10 차지한다는 의미이다.
[실습]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style type="text/css">
.flexContainer {
display: flex; /* div가 inline-block 특성을 갖게 된다. */
background-color: blue;
padding: 10px;
justify-content: center; /* 한 행에서 좌우, 센터 배 */
flex-direction: row; /* default가 row 방향이다. */
height: 300px;
align-items: center; /* 탑, 미들, 바텀 */
}
.flexContainer > div {
background-color: white;
margin: 10px;
/* height를 안주면 부모 height만큼 길이가 늘어난다. */
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="flexContainer">
<div style="flex:1">1</div>
<div style="flex:1">2</div>
<div style="flex:3">3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
box-sizing: border-box; /* 패딩을 주더라도 박스 사이즈가 늘어나지 않도록 */
}
.header{
background-color: #bac8ff;
padding: 30px;
text-align: center;
color: white;
font-size: 2em;
}
.center {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
.center > .leftmenu{
list-style-type: none;
padding: 10px;
flex: 1;
}
.center > .content{
padding: 10px;
flex: 4;
}
.footer{
background-color: #bac8ff;
font-size: 2em;
text-align: center;
color: white;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header"><h3>Cities</h3></div>
<div class="center">
<div class="leftmenu">
<ul>
<li>London</li>
<li>Paris</li>
<li>Seoul</li>
</ul>
</div>
<div class="content">
<h1>London</h1>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
<p>London is the capital city of England. It is the most populous city in the United Kingdom, with a metropolitan area of over 13 million inhabitants.
Standing on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its founding by the Romans, who named it Londinium.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">Footer</div>
</body>
</html>※ Bootstrap ( == CSS Framework )
- 부트스트랩 그리드 시스템은 반응형까지 지원한다.
- 부트스트랩3은 grid 시스템 만들 때 float속성을 이용하고, 부트스트랩4부터는 flex-box를 적용했다. (큰 차이점)
※ Javascript
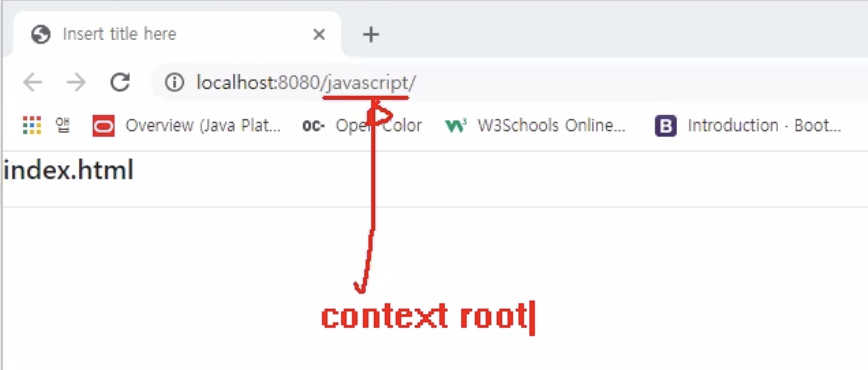
context : 실행 환경
▶ localhost - hostname
▶ 8080 - port 번호
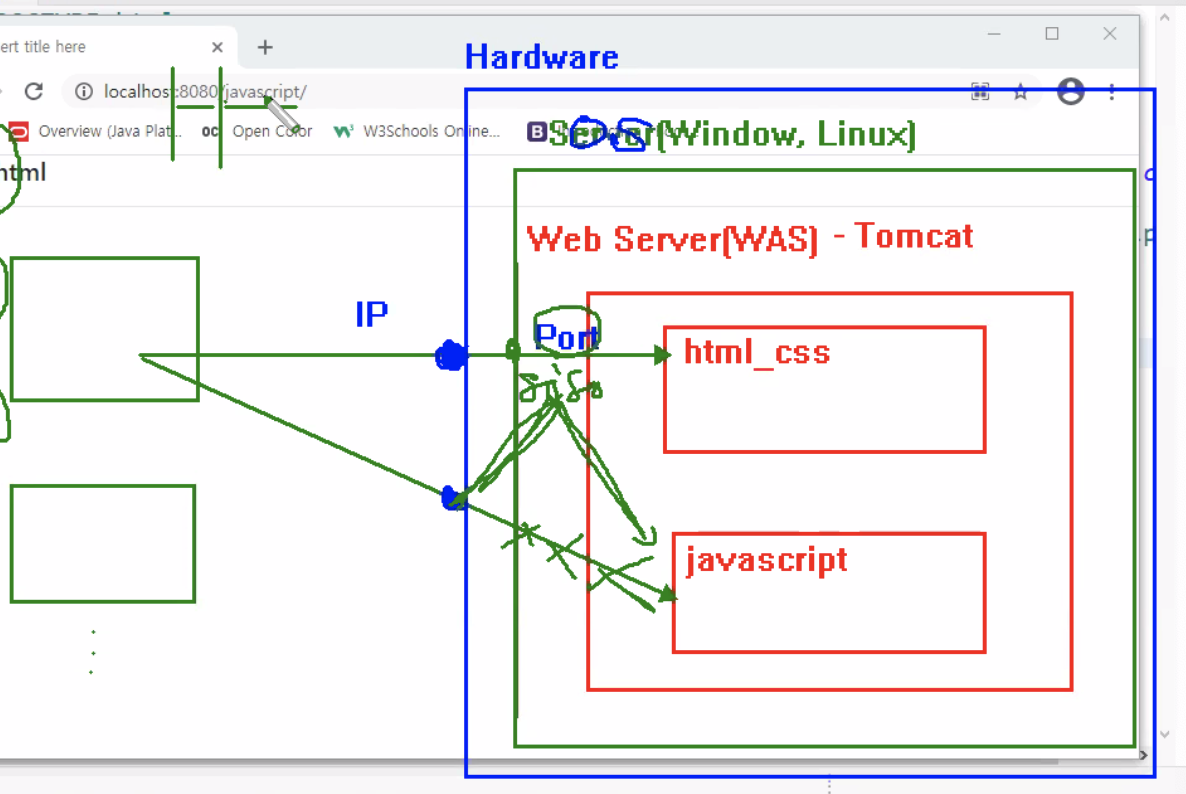
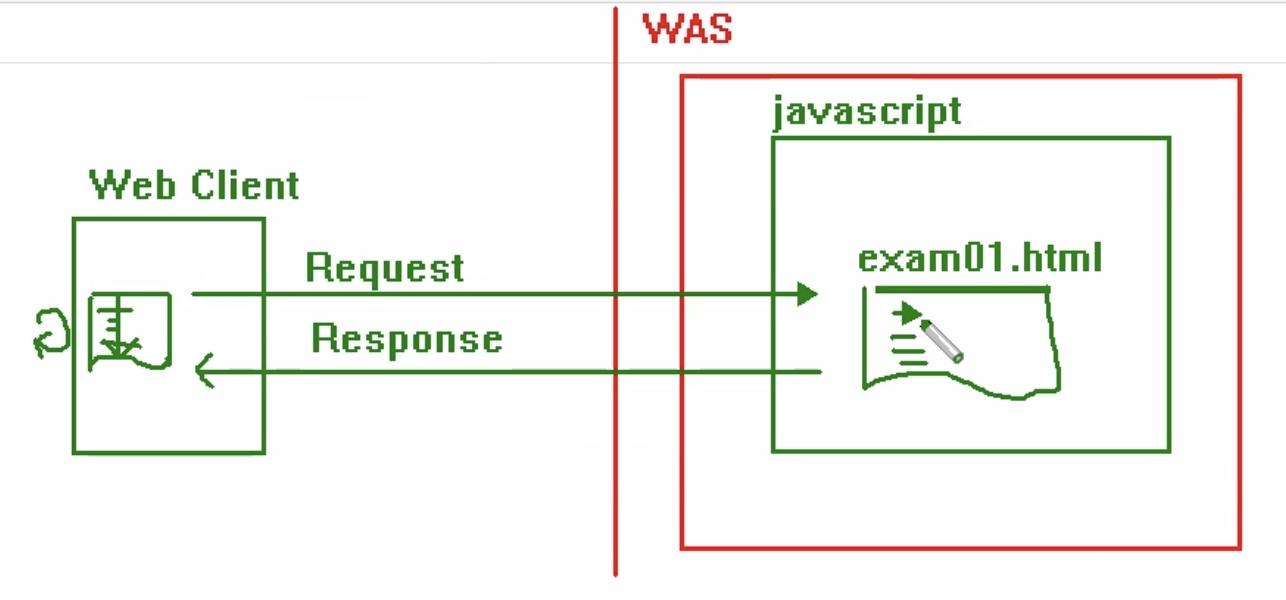
html 파일이 저장된 위치는 서버지만, 클라이언트에서 실행된다.
script부분은 브라우저에서 실행한다. 서버에서 실행하는 것이 아니다.
※ ES5, ES6 차이
▶ES5
2015 이전 문법(ES5: ECMAScript 5)
ES5 문법에서는 block level 제한이 없었다.
▶ES6
2015년 이후 문법 (ES6), block level 제한이 생김
=> let, const
<!--
html 파일이 저장된 위치는 서버지만, 클라이언트에서 실행된다.
script부분은 브라우저에서 실행한다. 서버에서 실행하는 것이 아니다.
-->
<body>
<h5>index.html</h5>
<hr/>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
console
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- 자바스크립트 작성 위치, 태그 주석 , 브라우저에 랜더링 되지 않는다. -->
<script>
/* 2015 이전 문법(ES5: ECMAScript 5)
ES5 문법에서는 block level 제한이 없었다.
*/
var var1 = 5;
var var2 = "홍길동";
if(true){
var var4 = true;
}
console.log(var1);
console.log(var2);
console.log(var3);
// 2015년 이후 문법 (ES6), block level 제한이 생김
let var4 = 5;
let var5 = '홍길동';
if(true){
let var6 = true;
// block level을 지원
}
console.log(var4);
console.log(var5);
console.log(var6);
</script>
<script>
// 2015년 이후 문법 (ES6)
const var7 = 5;
if(true){
// block level을 지원
const var8 = true;
}
console.log(var7);
console.log(var8);
</script>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
변수의 타입이 고정되는 것이 아니다.
변수를 선언할 때 타입을 지정해주지는 않지만 타입이 있다.
typeof는 변수의 타입이 아니라 변수안에 있는 값의 타입을 알려준다.
<script>
let var1 = 3.5;
console.log(typeof var1); //number type
let var2 = "JavaScript";
console.log(typeof var2); //string type
let var3 = false;
console.log(typeof var3); //boolean type
let var4 = {name: "Javascript"};
console.log(typeof var4); // object type
let var5 = function() {};
console.log(typeof var5); // function type
let var6 = () => {}; // arrow function 람다식 (너도 ES6 부터 생김)
console.log(typeof var6); // function type
</script>
[주의해야 할 연산 실습]
만약 연산자 앞이 부정이면(빈 문자열이거나 null 이거나 변수에 값이 저장되지 않으면)
"또는 (||)" 이니까 뒤에도 본다는 의미 => 뒤에가 답이 된다.
만약 연산자 앞이 true 의미이면 뒤에는 보지도 않고 앞에 답이 된다.
<script>
// 부정 || 값 => 값
console.log( "" || "abc"); // abc
console.log(null || "abc"); // abc
var var11;
console.log(var11 || 5); // 5
console.log(0 || 5); // 5
console.log(false || 5); // 5
// 긍정의 값 || 값 => 긍정의 값
console.log("a" || "abc"); //a
console.log(1 || "abc"); //1
console.log(true || "abc"); //true
// 부정의 값 && 값 => 부정의 값
console.log("" && "abc"); // 아무것도 출력되지 않음
console.log(null && "abc"); // null
console.log(false && "abc"); // false
// 긍정의 값 && 값 => 값
console.log("a" && "abc"); // abc
console.log(true && "abc"); // abc
</script>
★ 함수를 선언할 때 let으로 선언할 수 있지만, 함수의 번지가 바뀔 일이 없으니까 const로 선언하는 것이다.
[실습]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.0/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-B0vP5xmATw1+K9KRQjQERJvTumQW0nPEzvF6L/Z6nronJ3oUOFUFpCjEUQouq2+l" crossorigin="anonymous">
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.0/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha384-Piv4xVNRyMGpqkS2by6br4gNJ7DXjqk09RmUpJ8jgGtD7zP9yug3goQfGII0yAns" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.slim.min.js" integrity="sha384-DfXdz2htPH0lsSSs5nCTpuj/zy4C+OGpamoFVy38MVBnE+IbbVYUew+OrCXaRkfj" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.6.0/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-+YQ4JLhjyBLPDQt//I+STsc9iw4uQqACwlvpslubQzn4u2UU2UFM80nGisd026JF" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script>
console.log("hello, javascript1!");
</script>
<script src="exam01.js"></script>
<script>
function fun1() { // 함수를 선언하는 첫 번째 방법
console.log("fun1() 실행 ");
}
const fun2 = function() { // 함수를 선언하는 두 번째 방법
console.log("fun2() 실행 ");
}; // 함수를 참조하는 변수
const fun3 = () => {
console.log("fun3() 실행 ");
};
//------------------------------------------
function fun4(arg1, arg2){
console.log(arg1);
console.log(arg2);
};
const fun5 = function(arg1, arg2){
console.log(arg1);
console.log(arg2);
};
const fun6 = (arg1, arg2) => {
console.log(arg1);
console.log(arg2);
};
const fun7 = arg1 => console.log(arg1); // 매개변수가 하나면 괄호 생략 가능, 실행문이 하나여도 괄호 생략 가능
const fun8 = arg1 => console.log(arg1);
//------------------------------------------
function fun9(x, y){
return x + y;
}
const fun10 = function(x, y){
return x + y;
};
const fun11 = (x, y) => {
return x + y;
}
const fun12 = (x, y) => x + y; // 리턴 값인데 return 안써준다.
console.log(fun9(2, 3));
console.log(fun10(2, 3));
console.log(fun11(2, 3));
console.log(fun12(2, 3));
// 변수 선언은 세미콜론 붙이고, 함수선언이나 클래스 선언은 세미콜론 안붙여도 된다.
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
JavaScript Function
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- 함수 선언 방법 -->
<button onclick="fun1()" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun1()</button>
<button onclick="fun2()" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun2()</button>
<button onclick="fun3()" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun3()</button>
<hr/>
<!-- 매개값 -->
<button onclick="fun4('hello', 0)" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun4()</button>
<button onclick="fun5(5, 63)" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun5()</button>
<button onclick="fun6(true, false)" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun6()</button>
<button onclick="fun7({a:3, b:3})" class="btn btn-success btn-sm mr-2">fun7()</button>
<hr/>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
'Web > HTML & CSS & JS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Web] SSR, CSR 장단점 / 자바스크립트 아키텍처 (0) | 2021.05.18 |
|---|---|
| JQuery를 이용한 AJAX (비동기 통신) vs Promise 기반의 Axios (0) | 2021.03.14 |
| [JS] Call-Back Function/ JavaScript Promises/ 구조 분해 할당Destructuring / BOM & DOM (0) | 2021.03.10 |
| [JS] Study ES6(ECMAScript 2015) Using Reference (0) | 2021.03.09 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 자바스크립트Call-back
- @functools.lru_cache
- 객체지향개념
- jdk
- @functools.singledispatch
- method와 function
- yarn start
- Git
- sequelize.fn
- 익명자식객체
- 클래스와객체
- 인스턴스멤버
- nodejs
- dynamic-project
- 메이븐 저장소
- 자바빌드도구
- os
- @functools.wraps
- 자바스크립트Promise
- es6모듈
- 백준
- ES6
- 자바스레드
- 백준2206 파이썬 풀이
- 사용자정의예외클래스
- 생성자필드메소드
- java
- jre
- nunjucks
- 정적멤버
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
