티스토리 뷰
[JS] Call-Back Function/ JavaScript Promises/ 구조 분해 할당Destructuring / BOM & DOM
angelatto 2021. 3. 10. 18:56※ Call-Back Function (콜백함수)
: 직접적으로 호출하는 것이 아니라, 함수 내부에서 파라미터로 콜백 함수의 번지를 전달받아서 실행 흐름에 따라 자동적으로 호출하는 함수
▶ Synchronous (동기 방식)
: 위에서 아래 방향으로 실행하는 메인 흐름에서 어떠한 시점에 함수를 호출하면 메인 흐름은 실행되지 않고 응답(return)을 기다린다.
▶ Asynchronous (비동기 방식)
: 위에서 아래 방향으로 실행하는 메인 흐름에서 어떠한 시점에 함수를 호출하더라도 메인 흐름은 계속 실행되고,
이때 응답이 오면 그 때 처리를 해준다. 그 응답이 왔을 때 호출해주는 함수를 call-back 함수라고 부른다.
※ JavaScript Promises (ES6에서 새로 생김)
- 비동기 작업이 중첩되면 가독성이 떨어진다. 이를 해결하기 위해 Promise 라는 새로운 문법이 생겼다.
- 일반적으로 외부 라이브러리의 도큐먼트를 보고 리턴 타입이 Promise이면 then() 함수를 통해
내부적으로 작업이 성공했는가, 실패했는가에 따라서 각각 콜백함수를 호출해준다.
[방법1]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script>
const fun1 = () => {
/*
비동기 방식으로 콜백함수가 중첩되었을 때 가독성이 떨어지는 것을 보여주는 코드
console.log("코드1 실행");
setTimeout(function(){
console.log("코드2 실행");
setTimeout(function() {
console.log("코드3 실행");
}, 3000);
}, 3000); // 타이머 3초가 지나면 callback 함수를 실행하겠다는 의미
console.log("코드4 실행"); */
var promise1 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 시간을 요하는 작업
console.log("시간을 요하는 작업 ...");
var result = true;
if(result) {
resolve(); // success callback
}else{
reject(); // failure callback
}
});
/*
사실 일반적으로 promise1 변수에 담긴 함수는 베일에 쌓여져 있다. (외부 라이브러리, 비동기 작업, 네트워크 작업, 시간이 오래 걸리는 작업 )
내부적으로 성공적으로 실행이되면 promise.then(fun1, fun2)에서 자동적으로 fun1이 실행되고,
내부적으로 실패하면 fun2가 자동적으로 실행이 된다.
*/
// promise를 구현하는 방법 1
promise.then(
function() {
console.log("작업이 성공되었을 때 실행");
}, function() {
console.log("작업이 실패되었을 때 실행");
});
// resolve()가 실행되었을 때 파라미터 첫번째 있는 함수가 자동적으로 실행된다.
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
비동기 방식 이해하기
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<button onclick="fun1()" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm">
함수 호출
</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>[방법2]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script>
const fun1 = () => {
var promise1 = new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 시간을 요하는 작업
console.log("시간을 요하는 작업 ...");
var result = true;
if(result) {
resolve(); // success callback
}else{
reject(); // failure callback
}
});
// 방법2
/*
promise1.then(function(){ // 성공했을 때 실행
console.log("작업이 성공되었을 때 실행");
}).catch(function(){ // 실패했을 때 실행
console.log("작업이 실패되었을 때 실행");
}).finally(function(){
console.log("무조건 실행");
});
*/
promise1.then(() => console.log("작업이 성공되었을 때 실행")
.catch(() => console.log("작업이 실패되었을 때 실행")
.finally(() => console.log("무조건 실행"));
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
비동기 방식 이해하기
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<button onclick="fun1()" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm">
함수 호출
</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>[비동기 작업이 중첩되었을 때 문법 & 응답 데이터 넘겨주는 방법 - 1]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script>
// 우리는 fun2 함수의 리턴 타입이 Promise인 것만 알고 있고, 내부 코드는 모른다고 가정한다.
// 데이터 넘겨주기
const fun1 = () => {
fun2().then((response) => {
console.log("작업1이 성공되었을 때 실행");
console.log("실행결과: " + response.data);
return fun3();
})
.then((response) => {
console.log("작업2이 성공되었을 때 실행");
})
.catch(() => {
console.log("작업이 실패되었을 때 실행");
console.log("상태코드: " + response.statusCode);
})
.finally(() => console.log("무조건 실행"));
};
const fun2 = () => {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 시간을 요하는 작업
console.log("시간을 요하는 작업 ...");
var result = false;
if(result) {
resolve({statusCode: 200, data: "결과"}); // success callback
}else{
reject({statusCode: 404}); // failure callback
}
});
};
const fun3 = () => {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 시간을 요하는 작업
console.log("시간을 요하는 작업 ...");
var result = true;
if(result) {
resolve(); // success callback
}else{
reject({statusCode: 500}); // failure callback
}
});
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
비동기 방식 이해하기
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<button onclick="fun1()" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm">
함수 호출
</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>[비동기 작업이 중첩되었을 때 문법 & 응답 데이터 넘겨주는 방법 - 2]
- then 대신에 aync와 await 키워드 사용하는 방법
- 주의) 예외 처리하는 방식이 try-catch로만 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script>
// 데이터 넘겨주기
const fun0 = () => {
console.log("작업0이 실행됨");
fun1(); // 비동기 함수 , 안기다려줌
console.log("작업3이 실행됨");
};
// fun1 자체는 aysnc가 붙어있으면 비동기 함수라는 의미
// 하지만 그 비동기 함수안에서 fun2와 fun3의 실행 순서는 정해져 있다.
// async 없이 await를 쓸 수 없다.
const fun1 = async () => {
try{
var response1 = await fun2(); // fun2의 응답을 기다리겠다는 의미
console.log(response1);
var response2 = await fun3();
console.log(response2);
}catch(response){
// 에러가 아니라 reject을 했을 때 파라미터로 넘겨주는 데이터를 의미한다.
if (response.status === 404){
console.log("페이지가 존재하지 않음");
}else if(response.status === 500){
console.log("실행 오류가 발생 했음");
}
}
};
// 도큐먼트를 보고 리턴 타입이 Promise이면 위에 then() 함수를 작성할 수 있어야 한다.
const fun2 = () => {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 시간을 요하는 작업
console.log("시간을 요하는 작업 1 ...");
var result = false;
if(result) {
resolve({statusCode: 200, data: "작업1 결과"}); // success callback
}else{
reject({statusCode: 404}); // failure callback
}
});
};
const fun3 = () => {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
// 시간을 요하는 작업
console.log("시간을 요하는 작업 2...");
var result = true;
if(result) {
resolve({statusCode: 200, data: "작업2 결과"});// success callback
}else{
reject({statusCode: 500}); // failure callback
}
});
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
비동기 방식 이해하기
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<button onclick="fun0()" class="btn btn-danger btn-sm">
함수 호출
</button>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>※ 자바스크립트 구조 분해 할당 (Destructuring - ES6)
★★★★☆
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script>
// 배열 구조 분해 할당 1 - ES6에서 새로 생김
var arr1 = [10, 20];
/* var x = arr1[0];
var y = arr1[1]; */
var [x, y] = arr1;
console.log("x: ", x);
console.log("y: ", y);
// 배열 구조 분해 할당 2
var arr2 = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
var [x, y, ...rest] = arr2; // (용어 정리) ...: rest operator
console.log(x);
console.log(y);
console.log(rest); // [30, 40, 50] 배열
var arr3 = [...arr2, 60, 70]; // (용어 정리) ...: spread operator
console.log(arr3);
// 객체 구조 분해 할당
var obj1 = {x:3, y:5, z:7};
/* var x = obj.x;
var y = obj.y; */
// 속성의 이름과 변수의 이름이 같아야 값이 들어간다.
var {x, y} = obj1;
console.log(x);
console.log(y);
var obj2 = {...obj1, x:4, y:9};
console.log(obj2); // {x:4, y:9, z:7} 값 바꿀 수 있음
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
구조 분해 할당
</div>
<div class="card-body">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>※ 자바스크립트 BOM & DOM
▶ JavaScript HTML DOM => Document Object Model
Dom은 html을 브라우저가 해석해서 태그들을 어떻게 객체로 생성해야 하는지에 대해서 나타냄

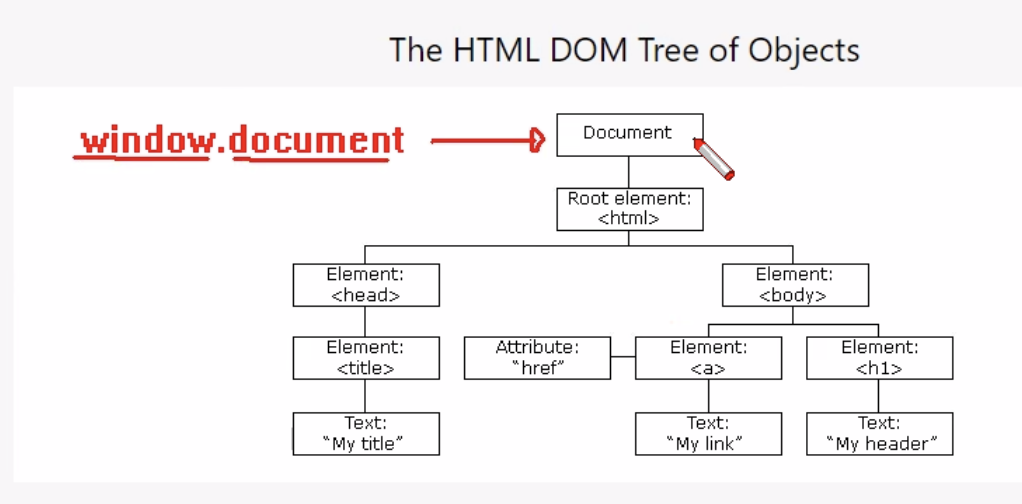
- 클래스 이름이 Element 이다. 태그를 Element 객체로 만들어라
- Document 객체가 최상위 객체이다.
- Document 객체를 참조하는 방법은 window.document로 참조를 얻는다.
▶ JavaScript Browser BOM => Browser Object Model

=> W3C에서 DOM과 BOM을 미리 정의해놈.
개발자는 여기에 정의해논 그대로 개발하면 다양한 브라우저에서 실행가능하다.
※ 1. BOM (Browser Object Model )
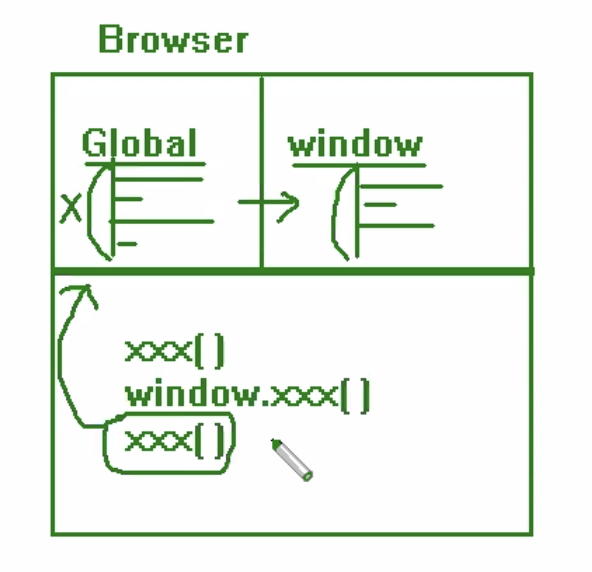
global에서 찾아보고 => 없으면 window에서 찾는다.
window 함수는 window.xxx() 도 가능하고, xxx()도 가능하다.
★☆ 꼭 알아두기
[JavaScript Global Functions]
1. parseFloat()
: 문자열을 실수로 바꾸는 것
2. parseInt()
: 문자열을 정수로 바꾸는 것
www.w3schools.com/jsref/jsref_obj_global.asp
JavaScript Global Reference
JavaScript Global Reference The JavaScript global properties and functions can be used with all the built-in JavaScript objects. JavaScript Global Properties Property Description Infinity A numeric value that represents positive/negative infinity NaN "Not-
www.w3schools.com
[BOM Window Functions]
cf> content area (viewport) : 뷰포트는 브라우저에서 딱 내용이 나오는 부분
※ Window Object Properties
| innerHeight | Returns the height of the window's content area (viewport) including scrollbars |
| innerWidth | Returns the width of a window's content area (viewport) including scrollbars |
| location | Returns the Location object for the window (See Location object) |
| navigator | Returns the Navigator object for the window (See Navigator object) |
※ Location Object Properties
[Property]
| hash | Sets or returns the anchor part (#) of a URL |
| host | Sets or returns the hostname and port number of a URL |
| hostname | Sets or returns the hostname of a URL |
| href | Sets or returns the entire URL |
| origin | Returns the protocol, hostname and port number of a URL |
| pathname | Sets or returns the path name of a URL |
| port | Sets or returns the port number of a URL |
| protocol | Sets or returns the protocol of a URL |
| search | Sets or returns the querystring part of a URL |
[Method]
| assign() | Loads a new document |
| reload() | Reloads the current document |
| replace() | Replaces the current document with a new one |
※ opener & open()
opener -> window의 프로퍼티
window.open() -> window의 메소드, 팝업창을 만든다.

open(url, 이름, spec);
※ 2. DOM (Document Object Model )
- Element 객체를 찾는 것이 중요하다
그 방법 5가지 중요
| getElementById() | Returns the element that has the ID attribute with the specified value |
| getElementsByClassName() | Returns a HTMLCollection containing all elements with the specified class name |
| getElementsByTagName() | Returns a HTMLCollection containing all elements with the specified tag name |
| querySelector() | Returns the first element that matches a specified CSS selector(s) in the document |
| querySelectorAll() | Returns a static NodeList containing all elements that matches a specified CSS selector(s) in the document |
[실습]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
<script>
const changeImg1 = () => {
//var img1 = window.document.getElementById("img1");
var img1 = window.document.querySelector("#img1");
img1.src = "/javascript/common/images/photo2.jpg";
};
const changeGroup1 = () => {
//var group1 = document.getElementsByClassName(".group1");
var group1 = document.querySelectorAll(".group1");
console.log(group1); // type : HTMLCollection
for(var i=0; i<group1.length; i++){
group1[i].src = "/javascript/common/images/photo4.jpg";
}
};
const changeImg = () => {
var imgs = document.getElementsByTagName("img");
for(var i=0; i<imgs.length; i++){
imgs[i].src = "/javascript/common/images/photo5.jpg";
}
};
const changeCssSelector = () => {
//var group1 = document.getElementsByClassName(".group1");
var group2 = document.querySelectorAll("#div3 > .group1");
console.log(group2); // type : HTMLCollection
for(var i=0; i<group2.length; i++){
group2[i].src = "/javascript/common/images/photo6.jpg";
}
};
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
Global Function 사용하기
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- 버튼과 이미지는 모두 인라인 요소 -->
<button onclick="changeImg1()" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">그림 변경 </button><br/>
<img id="img1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo1.jpg" height="100"/>
</div>
<hr/>
<div class="card-body">
<button onclick="changeGroup1()" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">그림 변경 </button><br/>
<img class="group1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo1.jpg" height="100"/>
<img class="group1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo2.jpg" height="100"/>
<img class="group1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo3.jpg" height="100"/>
</div>
<hr/>
<button onclick="changeImg()" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">모든 그림 변경 </button><br/>
<hr/>
<div id="div3">
<button onclick="changeCssSelector()" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">그림 변경 </button><br/>
<img class="group1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo1.jpg" height="100"/>
<img class="group1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo2.jpg" height="100"/>
<img class="group1" src="/javascript/common/images/photo3.jpg" height="100"/>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>'Web > HTML & CSS & JS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Web] SSR, CSR 장단점 / 자바스크립트 아키텍처 (0) | 2021.05.18 |
|---|---|
| [JS] Javascript/ ES5와 ES6의 차이/ CSS Flexbox (0) | 2021.03.14 |
| JQuery를 이용한 AJAX (비동기 통신) vs Promise 기반의 Axios (0) | 2021.03.14 |
| [JS] Study ES6(ECMAScript 2015) Using Reference (0) | 2021.03.09 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 자바스크립트Call-back
- nodejs
- nunjucks
- os
- 자바스크립트Promise
- 메이븐 저장소
- 익명자식객체
- 백준
- jre
- java
- 정적멤버
- 클래스와객체
- 생성자필드메소드
- Git
- @functools.singledispatch
- method와 function
- @functools.wraps
- jdk
- 인스턴스멤버
- yarn start
- 객체지향개념
- ES6
- @functools.lru_cache
- 백준2206 파이썬 풀이
- sequelize.fn
- 자바스레드
- es6모듈
- 사용자정의예외클래스
- dynamic-project
- 자바빌드도구
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
